Biostat 823 - Data Warehousing
Hilmar Lapp
Duke University, Department of Biostatistics & Bioinformatics
2024-09-12
OLTP vs OLAP
| OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) |
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) |
|---|---|
| Real-time data transactions | Data analysis (BI) |
| Fast response times, protected data integrity | Dataset generation for question answering |
| frequent INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | SELECT, frequently aggregated |
| Highly normalized design | Denormalized design |
| Constantly updated | Read-only, periodically refreshed |
Data Warehousing
- Data Warehouses support OLAP use-cases and applications.
- Typically built by ETL or ELT process(es)
- Often from multiple source databases
- Denormalized database schema design based on fact and dimension tables
Extract–Transform–Load (ETL)
Often uses staging tables and/or databases
Transformation in external software or in SQL
Note that tables can be created directly from query:
Datamarts vs Data Warehouse
- Datamart is a type of Data Warehouse
- Datamarts are typically more narrow in data scope
- Typically focused on one subject area
- Easier and less time-consuming to build
- Less memory and storage-intensive than a full Data Warehouse
![]()
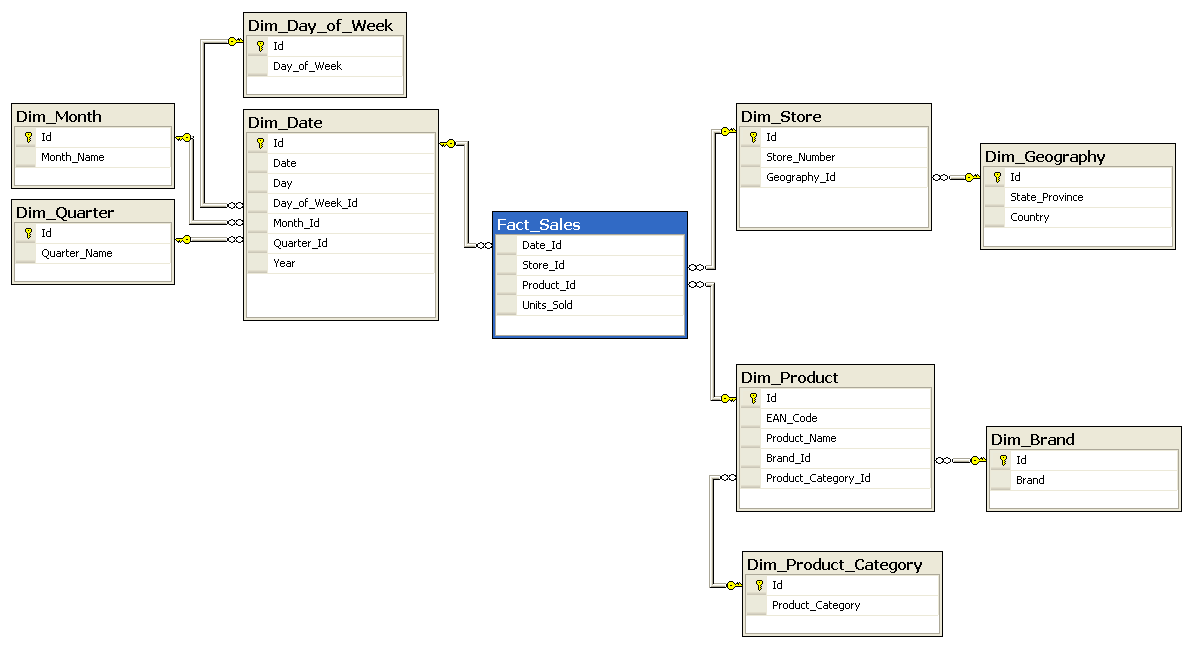
Star Schema
- Uses one (central) Fact table and multiple Dimension tables
- Fact table houses quantitative metrics or measurements
- Typically aggregated, based on chosen granularity (of dimension(s))
- Foreign key to each dimension
![]()
- Dimension tables house the dimensions along which to aggregate or slice facts
- Time, location, people, etc
- Typically denormalized
- Each dimension table has 1:n relationship to the fact table
- Fact table normally has orders of magnitude more rows than dimension tables
- In essence, this represents a data cube
- Fact table is the cells; dimension tables are the dimensions (“axes”) of the cube
Star Schema example (generic)

Clinical data warehouse example

Figure 1 from Hart and Kuo (2016), “Meeting Health Care Research Needs in a Kimball Integrated Data Warehouse,” 2016 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA) doi: 10.1109/DSAA.2016.91
Snowflake Schema
- A Snowflake Schema is a Star Schema with more denormalized dimension tables
From Wikipedia, Example of a Snowflake Schema by SqlPac
Reverse Star Schema
- Deployed for descriptive or observational facts
- Quantitative metrics often are not meaningful
- Typically multiple related facts (“dimension” table rows) for the central fact
![Figure 1 of Zhang et al (2011), BioMart: a data federation framework for large collaborative projects. doi:10.1093/database/bar038 Figure 1 of Zhang et al (2011)]()
- Queries often involve attributes of the central fact
- Fact table has 1:n (“reversed”) relationship to each “dimension”
- Hence, fact table is usually smaller than any of the dimension tables
Data Warehouses in Bioinformatics
- Many biomedical and biological data warehouse systems follow the Reverse Star Schema model

Figure 8 from Kasprzyk et al (2004) EnsMart: A Generic System for Fast and Flexible Access to Biological Data. Genome Res. doi:10.1101/gr.1645104
Genomics Data Warehouse systems
- BioMart (successor of EnsMart)
- Zhang et al (2011) BioMart: a data federation framework for large collaborative projects, Database, doi:10.1093/database/bar038
- Underlying the data mining UI and API for Ensembl (see also fully normalized Ensembl data model)
- Intermine
- Smith et al (2012) InterMine: a flexible data warehouse system for the integration and analysis of heterogeneous biological data. Bioinformatics 28(23):3163-3165
- Uses a configurable object-relational model, implemented in a PostgreSQL database
- Data access is through APIs
- Underlying the data mining API and UI for Drosophila, and deployed for dozens of other model organism databases
- See also Triplet and Butler (2014) A review of genomic data warehousing systems. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 15(4):471–483


